
The operation of making leather in which a lot of water is consumed and eliminates impurities and useless parts of the skin is called “soaking” operation. In water soaking operations, it has the most important role and effect on the quality of the skin and the final leather. Due to the importance of water, water used in leather production should have its own properties. For example, in the “soaking” stage, the hardness of the water must be between 12-18 degrees German to be able to play its role. Different stages of construction require the use of some very natural chemicals.
In the “soaking” operation, the first step is to open the parts of the skin that are stuck and folded, and then soften the hard, dry and dry skin. The faster the skin softening operation, the easier it is to maintain the skin. If the softening and wetting time of the skin is long, auxiliary chemicals should be used to reduce the average wetting time.
If the skin is fresh, it is not necessary to use chemical auxiliaries. But if the skin is dry, then moisturizers and antibacterial agents should be used. For dry skin use a lot of auxiliary substances and for fresh skin do not need these substances. For salted skins, the amount of ingredients is between the two.
Whether the skin gets wet in a paddle or drum and green lash is done or not, all affect the quality and duration of skin wetting.

Socking is actually the first practical step to start making leather. Many factors can affect the quality of sucking, some of which are listed below.
– Raw skin condition
– Quality of skin care and transportation
– Quality of water consumption
– Effect of ambient temperature and suction water temperature
– pH effect
– The effect of acidic and alkaline substances
– Effect of active surface materials (detergents and soaps)
– Use of enzymatic and antibacterial substances
– The effect of mechanical movements
In addition to the above factors, the effect of sucking aids should also be considered.
In the soaking stage, the condition of the skin plays a major role. Whether the skin is light or heavy has a very high effect on soaking. For example, heavy and thick skin is harder to wet than light skin. Freshly slaughtered cow skin is easily soaked in a shorter time than salted cow skin.
Air-dried cowhide will have problems getting wet. In soaking such skin, the use of auxiliary chemicals becomes mandatory. If there is excess meat and fat left on the side of the slaughtered skin, in this case it will be difficult to soak such skins due to the waterproof properties of the fat on the side of the body. Therefore, in the parts of the skin where these cases are seen, the wetting will be longer than other parts.
It is very useful to use the green lash method to prevent all parts of the skin from getting wet evenly and for ease of work in the next steps. By doing the green lash, the sucking time is reduced. The quality of sucking is uniform in all parts of the skin and lime is even.
If the green leash is not done, then major problems will occur. Moisturizing is usually difficult and non-uniformity is seen in different parts of the skin in terms of quality.
Today, efforts are being made to do green lash work in slaughterhouses. The skin, which weighs 35 kg, has 5-6 kg of green skin. Of this amount, about 1.5 kg is fat. The green lash of softened salt skins is easier to do than fresh skins. Because fresh skin is very soft and does not stand still under the device. The soaked salt skins are first soaked for 20-30 minutes to open the sticky parts and the salt in the labia of those parts is removed and then the green stain is applied.
These operations include removing the gamble, which is the green color of the skin, as well as opening the skin. On the other hand, a device called machine structure is used to open the skin, especially light skin. Using this device on light skin is actually a kind of green leash. With the difference that only fats and very large lumps are removed from the skin. This makes the leather have a higher surface and the extracted wool has a better quality. Instead of a machine structure, a slow-moving blade machine can be used.
How to dry, transport and store the skin Before the skin dries, a large amount of bacteria is found in it. When soaking, the activity of these bacteria, which was shut down during drying, resumes. If the drying is not done properly or the amount of salt consumed is not sufficient and suitable for salting, the bacteria activity will continue during transportation and storage.
Bacterial activity during storage causes hydrolysis of skin collagen. Therefore, salting or drying the skin is very important. When transporting the skin due to air currents, the sides and even the sun may dry the skin from the middle parts. Due to the non-uniform dryness of the skin in different parts of it, many problems occur when soaking. To prevent this, when transporting the skin, all parts of it should be covered with a suitable cover. If the skin stays in the ketone state for a long time in the open air, its sides will dry again and it will become twisted. In this case, the dried parts are not wet well and easily compared to other parts.
Water is used to soak raw skin and clean it of associated impurities. In the leather industry, the amount of water consumed at each stage is very important. In general, it can be said that each kilogram of raw skin consumes 5-8 kilograms of water. In the leather industry, the ratio of water to skin is flute (bath). For example: If the flute is low:
– The concentration of water-soluble substances increases and the transfer of soluble substances inside the skin into the bath becomes difficult.
– Due to the lack of water, mechanical movements are not performed properly and as a result, the fibers do not open well.
– Antibacterial agents and sucking aids are not distributed evenly and evenly between the skin and its fibers.
– Due to the weight of the skin and its insufficient floating in water, mechanical movements are difficult and the electromotor of the device is affected.
– Production operations are limited or lose their efficiency due to time consuming.
Due to the dilution of the salt in the bath, spherical proteins dissolved in water are not completely removed.
– Due to dilution, the amount of antibacterial substances and auxiliary substances lose their effectiveness.
– Production cost increases.
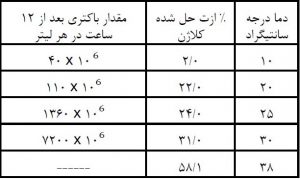
Temperature in Celsius Percentage of nitrogen dissolved in collagen The amount of bacteria per liter after 12 hours
10 2 40*106
20 22 110*106
25 24 1360*106
30 31 7200*106
38 58.1 —–
As can be seen in Table 1-1, collagen hydrolysis is not noticeable up to 25 ° C, but from this point on, collagen hydrolysis begins, and this is due to the rapid increase in bacterial activity.
Author: Mr. Ebadollah Yousefzadeh, Professor of Leather University