
Today, the manufacture of leather from fish skin (sturgeon) and reptiles is almost one of the tasks that is more or less common in places where the leather industry has changed from traditional to industrial. The production of leather and leather goods from the skins of fish, lizards and crocodiles, including sturgeon, accounts for a large proportion of decorative leather products. In the meantime, ostrich skin should also be considered, as shoes and bags made of leather have their own beauty.
Although the production and manufacture of decorative leathers from the skins of fish and reptiles has been popular around the world for a long time, but due to economic and market issues, not much has been published in this regard. According to some informed people, apparently more than 80% of sturgeon species live in the Caspian Sea and the remaining 20% is distributed throughout the world’s waters. Using caviar as the best and most quality export commodity, using sturgeon skin in leather making and its consumption in handicrafts, using bone and fish fins in preparing poultry feed and using its meat to provide white protein. It is a sturgeon.
In this article, in addition to describing the steps of making leather, it is tried to provide information about how to peel and how to preserve and maintain the skin of fish and other side issues. The presented materials are all based on experiences and the results of laboratory work.

Any of the following methods can be used to make leather from sturgeon skin. Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages. Each of the following methods has been used in making the presented samples. The best results are obtained when the best advantages of each method can be applied in a single formulation.
In chrome tanning, the steps of making leather from the skin of sturgeon are almost the same as the steps of making animal skins. In this method, chromium penetrates very well into different parts of the fish skin, especially to the parts that have a white texture, and burns it evenly from head to toe. The wrinkling point of such leathers reaches 75 degrees Celsius, which is the highest wrinkling point compared to other methods.
The main disadvantage of these methods is that, firstly, the chrome color covers the natural color of the skin, and secondly, if the necessary care is not taken in the neutralization stage, chromium will deposit on the mat-shaped textures. Despite these two major drawbacks, elephant skin can be easily tanned this way. First of all, the natural color of elephant skin is not very interesting; And secondly, in the finishing stage, using the finishing methods, the desired leather color can be produced.
Aluminum penetrates the skin of fish less than chromium. When using alum in parts of the fish skin that is full, the problem of tanning increases. Consumable aluminum sulfate dries tanned leather. Therefore, in this method, the lubrication stage and the types of oils used are very important. If care is not taken in the degreasing and lubrication steps, the leather produced will later be like a dry board.
Alum has water-absorbing properties, and tanned leathers may swell and become uneven after a while due to moisture absorption. With all these disadvantages, the biggest advantage of using alum is that the natural color of the leather is preserved. Some sturgeon skins are not tanned this way. This method is more suitable for elephant skin. Ozone skin and sturgeon do not work this way.
If high purity aluminum sulfate or modified forms such as Lutan B are used with aldehyde tanning materials and suitable oils are used in the lubrication stage, a better result will be obtained. The wrinkling point of the above leathers is 62-70 degrees Celsius.
Mimosa powder is usually used in vegetable tanning. The result is very good on sturgeon skin and ozone. If there is no problem in the pre-tanning (sucking-liming) stages, the tanned vegetable leather will soften completely. So that this leather is almost no different from animal leathers.
In the skin of elephant fish, because the thickness of the white parts under the abdomen and the colored part of the back are very different from each other, the speed of penetration of tanning materials in these two parts is different.
This causes the colored part to absorb more material and as a result one side of the fish skin becomes full and heavy. While the other side, especially the earlobes (parts covering the gills) are not tanned and remain raw. Vegetable tanned leathers are similar to beef leathers. Due to the excessive absorption of mimosa and the dominance of its color over the natural color of the skin, the appearance of the produced leathers is not pleasant and this problem cannot be solved in the complementary stages. Due to the above considerations, the use of vegetable tanning materials in making leather from sturgeon skin is not recommended.

This method uses different types of replacement tanning agents. Materials such as Irgatan Lv from CIBA, Cotritan IN from CHROMOS ZAGREB and Basintan DLE from BASF are very suitable for this purpose. In using the above materials as tanning materials, the use of aldehyde tanning agents in the ethanation stage is essential. The above materials often
They have derivatives of annihilation. These substances, when the enzymatic step does not work well, instead of penetrating the leather, they deposit on its face and cause cracking of the leather face during the tanning operation. The best way to prevent cracking of the leather face is to use aldehydes such as Relugan GT50 in the protonation stage.
Using soft tanning agents such as Relugan RE before adding phenolic tanning agents to the tanning bath also prevents cracking of the leather face. In this method, the color of the aldehyde solution is combined with the color of syntene until they turn yellow in the light and changes the natural color of the skin. In many cases, this color change makes the skin of the fish look beautiful.
In the finishing stages, due to the oxidation of the raw fat on the sides of the bone rows, a sharp tan color is formed around these bones. The presence of this color along with the previous background color makes the appearance of fish skin very beautiful. The use of polymer and melamine synthene synthetics causes leather fullness and softens the leather face. The wrinkling point of these leathers is between 62-65 ºC.
Aldehyde tanning is one of the most suitable methods for all skin types of fish, including sturgeon. In this method, while the skin retains its appearance, the disadvantages of previous methods such as cracking occur in the tanning method with syntheses, the possibility of chromium deposition, chromium tanning, hardness and moisture absorption of the aluminum method and removal of natural color in the tanning method It does not have a plant.
However, the use of glutarone aldehydes turns the skin yellow. It is better to use formaldehyde for tanning and use colorless synthetes to fill the leather during the retaining stage. The wrinkling point of tanned leathers is C70 aldehyde. The only major drawback of this method is that the use of formalin has many environmental issues; And in some countries the use of this substance is prohibited.
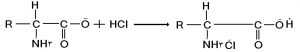
This method uses oily materials that have both tanning properties and are used in the lubrication stage. In the retanning of leathers that are tanned with oil, soft and colorless syntheses are used.
The main disadvantage of this method is that the leather becomes colorless or pale even after the completion of the finishing step due to stretching or folding at the place of folding or stretching (Pull up mode). This is an advantage in sheepskin; But in the leather of shoe uppers and sturgeon skin, it reduces the value of work.
Materials such as Amorgan A are very suitable for this purpose.
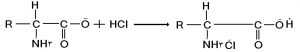
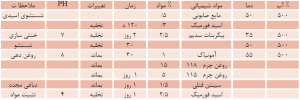
Using any of the above methods is very effective. However, it seems that using a combination of different methods to make leather from the skin of some species of sturgeon is better and for some species only method (4-5) should be used. In general, it can be said that the specific characteristics of different species of sturgeon determine the method and method of tanning the skin of sturgeon. Experiments show that different types of fish skin are placed in the same solution of salt water and sulfuric acid at pH = 3.
After 24 hours, each of the above solutions shows a different pH. For example, solutions in which elephantfish skin or challah skin is placed, after 24 hours, their pH increases from 3 to 4.7 – 2.4, while solutions in which dice shells Fish or ozone or cranberries will have a pH between 6.6 – 6.2. The highest pH is related to the solution containing ozone. (PH = 6) Considering the above, it turns out that acid absorption is different in different species and this may be related to free carboxylic groups in skin collagen.
Given that the description of this article requires sufficient knowledge of animal biochemistry and histology, and we have the ability, to justify the different pH changes of the above identical solutions, we assume that the collagen amino acids of normal skin are as follows:
As the acid increases in solution and gradually penetrates the skin fibers, the poles of the amino acid molecule absorb their non-homonymous ends: Obviously, the higher the carboxylic group, the more H is absorbed, and as H is absorbed from the medium, the pH of the solution increases until the high reaction reaches equilibrium. After equilibration of the above reaction, the pH of the solution (medium) remains constant.
According to the pH difference of the experimental solutions, it can be concluded that the skin of ozone absorbs / 1000 times more acid than the skin of elephant fish and in other words, the skin of ozone / 1000 times more than the skin of elephant fish has free carboxylic group.
Perhaps this is why when alum is used to tan ozone, more molecules of alum are absorbed into the skin, and because alum is a brittle fuel, it becomes hard and brittle because of the leather produced. While in the skin of elephant fish this condition is almost not seen. Based on this, it can be said that the specific characteristics of different skins determine its tanning method.
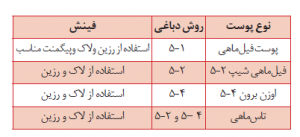
Based on the results of experiments and work performed and taking into account the presented materials, the following division is suggested as a general guide for tanning different types of sturgeon skins:
Despite the above table, the best method of tanning is to first tan the skin with oil and then tan with aldehyde, and in the next step to retan with suitable synthetes. This method is true for most species. In the case of ozone, this may be the only tanning method.
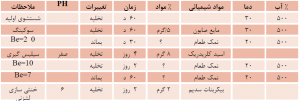
This is done for several purposes. First, the outer surface of sturgeon skin is covered with a thin layer of fat that makes it slippery. To remove this fat, sucking and using fat-absorbing substances in it is necessary.
Second, when fishing, a lot of fine sand sticks to the animal’s body. In the sucking stage, the sand is washed and removed. Dry salt skins must be thoroughly soaked to continue the process. The average time required for this is 2 days and nights, which can be doubled depending on the storage period and skin type. The use of antibacterial agents in the sucking stage is essential. Unlike animal skins, sturgeon skins are better in saline solution. This may be due to the compatibility of the saline solution with the fish’s habitat.
If the salt water plant is higher than 7 and with increasing sodium carbonate, the pH of the environment reaches 10-9.5. Suitable conditions are created for sucking. It is better to soak the skin overnight in a solution of salt water with pH = 10 and overnight in the absence of salt and only in a solution that has a pH of 10.
If the pedaling is done due to a series of disturbances, the work is done better. Good sucking Introduction Tanning is right. If sucking is done in the jar, its duration should be multiplied.
Experiments and experiments show that if silicification (softening of bones) is done after sucking, it will be useful for two reasons: First, after the softening of the bone, the crushing is done easily and the mechanical movements on the skin do not damage the rows of the bones, and second, the skin can be kept for a long time during the silicification stage. The silica trap is mostly used to make leather from the skin of crocodiles, which contain hard cartilaginous material. This stage is almost like a pickling stage.
The difference is that at this stage, hydrochloric acid must be used. Hydrochloric acid dissolves and removes calcium salts in cartilage and bone, making it soft. The higher the acid concentration, the shorter the effect time. To avoid acidic swelling, the skins should be soaked in brine for at least one hour, and the acid added gradually over 3-4 hours.
After each step, the acid must be controlled while stirring the pH solution. Until pH = 0. Due to the absorption of acid by the skin fibers, the pH of the environment increases. Therefore, the next day or days, while controlling the pH, it should be reduced to zero by increasing the acid.
The amount of acid consumed will depend on the acid concentration and the type and number of skin. Silicification takes 3 to 10 days. After the silica is removed, the skin is transferred to a salt water solution with boomeh 10, so that its pH is gradually increased.
Transfer of silica skin to brine solution causes the pH of the solution to increase to a maximum of 3.5-5. If the pH is raised for at least two days, possible acidic swelling will be prevented.
After two days, the skin is transferred to another saline solution with a grade of 7, and with a gradual increase in sodium carbonate, the pH of the environment is raised to 6-7. At this stage, care must be taken to equalize the pH of the environment and the cross section of the skin.

The neutralized skins of the previous stage enter the liming stage in the absence of salt, with the increase of sodium carbonate the pH of the environment reaches 10. If the skin stays in this state for 3 days and nights, the desired answer will be obtained. Liming may be performed using other strong alkalis such as sodium sulfide, lime, caustic soda, or a mixture of these; But experiments show that the use of sodium carbonate works best for the following reasons:
When sodium sulfide is used for liming, there is severe corrosion of the skin parallel to the row of bones, so that the skin is torn apart by the slightest stretching of the skin. This condition is also seen in the liming bath containing a mixture of sodium sulfide and lime; But its intensity is less than the first case. If caustic soda is used in liming, all other parts of the skin except the bones are destroyed.
If the concentration of soda is low, the surface texture of the skin disappears and the skin becomes a completely white patch of skin devoid of any pattern. Using lime alone makes the skin very soft and does not cause any damage to its texture.
But when the skin is tanned and oiled. Due to the lack of absorption of will oil other unknown issues after the production process, the resulting leather dries completely. According to the above, the best and easiest way of liming is to use sodium carbonate.
Peeling skin that has been peeled off by A or B is very easy. Of course, the skin must be rubbed along its length. In this case, both the bones are not damaged and the worker uses the machine without feeling threatened. The skill of the worker and the adjustment of the machine are important factors of a correct lashing. After washing, the skin is washed twice with 25 degrees water.
3-5 Deliming (Beating)
When enough sodium carbonate is consumed in the liming stage. The cross-sectional pH of the solution reaches about 10. In the delamination stage, like the delamination method of animal skins, while removing the alkaline substances, the pH of the environment and the cross section of the skin is raised to about 8-5-8.
The best means of delamination is washing the skin with water. If this operation is repeated two or three times, a better result will be obtained. However, the use of ammonium sulfate is very satisfactory. The amount of enzyme consumed depends on its biting power. Therefore, its consumption varies from 1 to 3 grams per liter of solution.
If the temperature of the bathing bath is 28-30 degrees and its operating time is 3-24 hours. A good result is obtained. When the temperature rises or the operation lasts more than a day, the skin smells. The effect of the enzyme should be recognized only by touching the skin with the hand. Bubble testing on fish skin may not be practical.

3-6 Degreasing:
Degreasing can be done in two ways:
3-6-1 Chemical degreasing:
Good degreasing can be done using water emulsion, a good naphtha solvent and a good emulsifier, provided that the ratio of naphtha solvent, emulsifying agent and water is considered 1: 1: 60, respectively. The fat in the appearance of the skin is completely removed. The result of good shooting can be seen at this stage.
Grease in the drum at 30 ° C gives better results than grease in exchange.
3-6-2 Physical degreasing:
This method is used only to remove existing and trapped fats in bone anticlines. Because elephantfish skin does not have many bones, it can be fattened without the use of a physical method, just by using a conventional chemical method. In the physical method, after the biting stage by dehydrating the skin, it is prepared for degreasing with a press. It is better to use two pieces of flat felt as the upper and lower pillows of the skin in the press machine to avoid damaging the skin and not contaminating the machine with fish skin oil.
A sheet of felt, while preventing damage to the skin, prevents the device from being contaminated with fish skin oil by absorbing the oil secreted by the skin. In this method, by applying pressure 100 times in 30 seconds, almost all the fats trapped in the bone anticlines come to the surface of the leather and are absorbed by the felt.
The Mustardini machine is very suitable for this purpose. It is possible to use the hydraulic power of the jack and two wide plates for this purpose. After pressing, the first method of degreasing should be used to remove the skin secreted fats. Thus, in fact, for good fat loss, both of the above methods should be used. Of course, it should also be borne in mind that skins that have large bones, while pressing these bones, break and when the bone is broken, fat penetrates to the surface of the skin. This condition is more common in the case of skins that are peeled by method A, and as a result, the resulting skin becomes deformed.
3-7 Pickling:
It is not necessary to salamander the skin of fish in making them, but this operation is one of the best ways to preserve the skin for a long time. Especially if hydrochloric acid is used instead of formica or sulfuric acid, it also helps soften bones and cartilage. When tanning the skin with chrome or aluminum, lawyers’s tanning with mineral tanning materials is necessary to piculate the skin, and in other manufacturing methods described earlier, there is no need to salamander.
If the pickling is to preserve the fish skin, then the brine should be at least 20 and the skin pH should be adjusted to 1-2; But if the pickling is only to prepare the environment for tanning with minerals. In this case, if the boom is 10-12 and 2 / 8-3 / pH = 2, it is enough. And the desired result is obtained.
3-8 Tanning:
In the section on manufacturing methods, various methods for making leather from sturgeon skins were described. What should be considered in all methods is that the lubrication is appropriate and timely. For example, in mineral tanning, be sure to use oils that are well resistant to acids at least 2 grams per liter of solution. In methods that do not require fish skin pickling, if oil tanning is used as a toning material.
You get better results. After the tanning, if the skin of the fish remains in the form of porcelain for at least 2 days and then goes to the retaining stage, a better result will be obtained.
3-9 Retanning:
This stage is no different from the retaning stage of light leathers, and since the natural color of the skin of sturgeon is desirable, no special dyeing is required. Of course, if a very small amount of acidic blue or green colors are used in dyeing, due to the combination of the natural color of the fish skin with the color added to the drum, a special pleasant color is obtained that greatly increases the value of the leather.
It is better to use soft syntheses in retaining. It is very convenient to use aldehyde tanning materials before syntheses, especially in the protonation stage. So that if naphthalene or phenolic derivatives are used in the absence or at the same time with aldehyde tanning materials such as Relugan GT50, the skin of sturgeon like desert lands will crack and the leather will be completely destroyed. Lubrication is done at a temperature of 50-60 ° C and its fixation is possible with formica acid.

4- Completing:
4-1 Pre-finishing Operation
If all the steps related to the preparation, maintenance and construction of sturgeon skin are done carefully, the produced crust will not need much finishing operation. The skin of fish with large or large rows of bones is usually defective when softening the shredder. It is better to mill this type of leather for a long time. The molten leather is clamped after softening. Because this type of fish skin is leached and can not be shaved, the leash side usually has lesions.
These excess materials must be removed by buffing. For uniform buffing, the glued leather should be pressed. An inlet pressure of 250 bar and a temperature of 100 degrees are suitable for this purpose. As a result, the pressing side of the leather body is completely smoothed and thus prepared for buffing. In buffing, due to the pressure and friction, the local temperature of the leather increases, and because its wrinkling point is low, the leather may lose its shape. Therefore, it is better to buffing with low pressure and evenly. Buffed leathers are prepared for finishing operations after dusting and trimming.
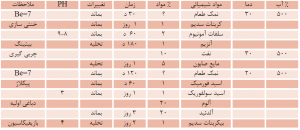
4-2 Finishing
The skins of sturgeon have a special natural pattern that does not require finishing. If anything is done in this regard, it is only to polish its surface. The use of soft resins and suitable waxes, especially the use of solvent varnishes, makes the leather shiny and waterproof. In some species, such as ozone skin and sturgeon, the use of varnish solvents makes the leather too beautiful.
Elephant skin loses some of its natural color during construction. Using suitable finishing materials such as pigments and resin binders, the leather can be made into a natural color to the desired level. In case of consuming large amounts of varnish, the leather loses its natural state. It is better to use solvent varnishes and for high gloss, press the finished leather several times at high temperature and pressure.
5- Making formulation:
1- Operation of wet part
A- Primary washing + Soo King + Sturgeon silicification This operation is performed in the pedal. Gram means grams per liter of solution per minute
B- Primary tanning:
The pellet obtained from the above operations is tanned in sturgeon according to the following instructions. This method is recommended as a universal method for tanning all species of sturgeon. Consumables are calculated based on the weight percentage of pelleted pellets.
C- The pellets obtained from the above operations, which are equivalent to the wet blue of animal leather, are stained for a week and then re-tanned according to the following program. The result is a crust. (Percentages are based on Wet Blue weight)
D- Finishing:
At this stage, only colorless resin and varnish are used to polish the leather.
Source used:
Recommended Recipes for the Production of Leather from Reptiles and Fish S kin B. ASF.Germany
Regarding the source used, it should be said that: This source offers suggestions on making leather for reptiles and fish. The fish in question in these suggestions is a shark. No recommendation has been provided for sturgeon. There are similarities between the skin of crocodiles and sturgeon. Therefore, the suggestions made were useful.
2- The source in question has not been published anywhere as a scientific source in books or as a research article. In addition, along with the release brochure of leather and chemical catalogs of BASF company, it has been provided to most leather manufacturers as a brochure.
The writer: Professor Ebadollah Yousefzadeh (Eng.) – University Professor